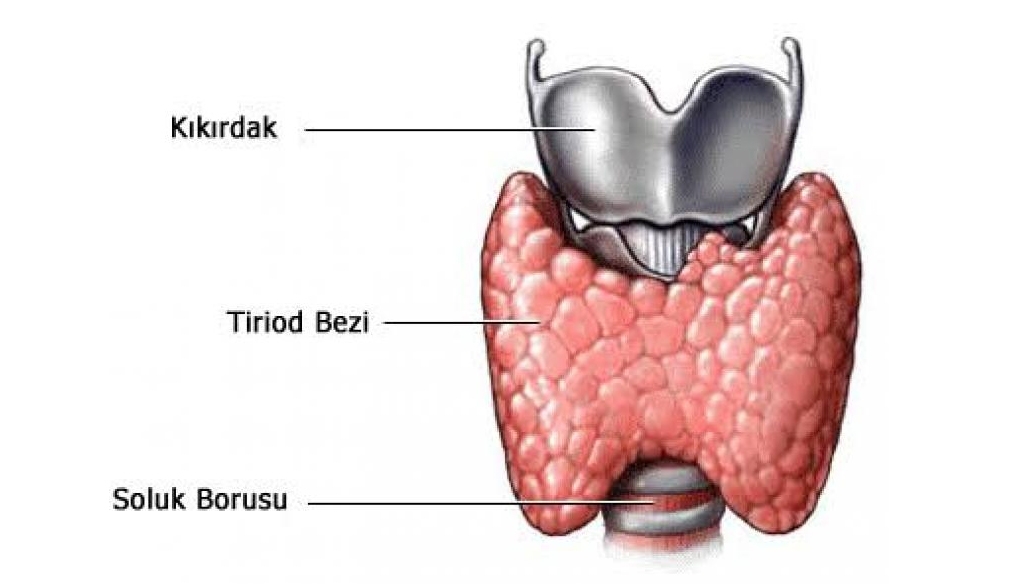
What is a goiter?
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front part of our neck. Its approximate weight is 20-25 grams. Its most important task is the production and secretion of the hormone thyroxine. This thyroxine hormone is responsible for regulating the metabolic functioning and speed of our body in general. The main purpose of our thyroid gland is to regulate the body’s energy consumption. The normal occurrence of the values of this hormone secretion is called Euthyroidism, its insufficiency is called hypothyroidism, its excess is called hyperthyroidism.
In medical parlance, the growth of the thyroid gland is called a goiter. If this growth is large enough to cover the entire gland, it may be diffuse and nodular if it is in a way that will form the shape of a chickpea grain in the gland.
What is goiter surgery, who can it be performed on?
The surgical removal of the thyroid gland, performed to provide treatment for structural or functional disorders of some goiter, is called thyroidectomy. This surgery is usually known as “goiter surgery” among the public. Dec.
In the thyroid glands, which are pressing on the neck and are enlarged
In patients whose treatment cannot be provided by using drugs for a long time
Patients whose thyroid gland exceeds 23 cm
People at risk of cancer, even if their nodules are small
It is necessary to perform thyroidectomy surgery on patients whose neck swellings are both aesthetic and dangerous.
How is goiter surgery performed?
For the operation, the patient is completely put to sleep and general anesthesia is used. The duration of the operation is usually between 90 and 120 minutes. Dec. Despite the undesirable situations that may occur after surgery, the patient should stay in the hospital for a day. The operation is performed by applying a 56 cm long horizontal incision to the front of the neck. In this way, the vessels of the thyroid gland are connected and cut, and a large part or all of the gland is removed. During surgery, it is important to carefully monitor and protect the parathyroid glands and the sound-making functions and nerves in close proximity to the thyroid gland. Another issue that should be considered is the removal of the entire gland if there is a suspicion of malignant disease.
A surgical technique in the form of removing cysts one by one during surgery is not suitable for surgery. But only unilateral surgery (right or left thyroid lobectomy) can be performed in patients where one of the two lobes of the thyroid gland appears completely normal during the examination, or on ultrasound.
Goiter Surgery Results And Problems
Effective and permanent treatment is provided for all patients with a properly performed surgery in a fully-fledged hospital. There is a possibility of recurrence of the disease after partial thyroid removal surgery (partial thyroidectomy), but it is very low. In the case of complete removal of the goiter gland (complete thyroidectomy), patients should take one tablet of medication (thyroxine hormone) every day for life, but there is no chance of recurrence of the disease.
Provided that the majority of the surgeries performed are temporary, hoarseness (nerve trauma) may develop in about one in fifty patients, and hand numbness (parathyroid gland damage, calcium deficiency) may develop in about one in fifteen patients. But although the probability of such permanent problems occurring in operations performed by experienced surgeons is almost zero, it is a very rare condition.
It is not possible to predict exactly in advance that there may be problems in patients applying for surgery. But these possibilities may increase in types of goiter, in which the thyroid gland may show intense adhesions to the surrounding tissues, and in patients who have had goiter surgery for the second time.
After goiter surgery in the hospital
The patient comes out of the operating room to the bed with his neck wrapped. Sometimes a plastic pipe (drain) with a diameter of 34 mm may be found extended outwards from near the edge of the wound. The reason for installing the drain is to remove leaks that may occur in the surgical area at an early stage with the help of a vacuum. The inserted drain is usually removed smoothly the next morning.
A few hours after leaving the operation, the patient completely regains consciousness, can talk and take food by mouth. The patient does not even need serum after 5-6 hours. After the operation, the patient can walk and move his neck freely. The patient’s relatives exhibit some strange beliefs such as that the patient should not move his neck after the operation, avoid making noise, and should not speak with information in his own way. But medically, the patient’s neck movements and speech are free. In general, patients do not experience a very severe pain problem. It is enough to take painkillers 2 to 3 times on the night of surgery. The patient who has undergone surgery is usually discharged the next morning.
Is goiter surgery unilateral or bilateral?
In our body, the thyroid gland consists of two round parts (bumps) that join at the midline of our height. With goiter surgery, one or both of them may need to be removed. The decision is usually made according to certain criteria before or during surgery. If there is a disease on both sides, the gland is completely removed.
In this way, the risk of developing a thyroid-related disease in the future also completely disappears. Another aspect is that the nerves leading to the vocal cords on both sides are at risk of being affected during the operation, and the disadvantages of the procedure are that the patient has to use pills every day for life if he encounters slippers after the operation.
If the disease occurs on one side, then one side can be removed by leaving the side that is not the disease in place. In these cases, the advantages and disadvantages of the complete removal of the gland surgery are replaced. Because of this, he does not have to use pills for life, and both of the nerves leading to the vocal cords are at risk not only on the operated side. The disadvantage of this surgery is that the possibility of developing the same disease again on the remaining side continues.
How should the preparations be before the operation?
If there are conditions requiring surgery in the patient and the patient’s hormone levels (t3, t4, tsh) are within normal limits, preparations for surgery can be started directly for the patient. But if there is an increase in hormone levels (hyperthyroidism, toxic goiter), it can be very dangerous to take the patient to surgery immediately. It should be ensured that the patient first passes the examination of an endocrinology or internal medicine specialist and that the hormone level becomes normal with drug therapy. Preferably, the patient should be operated on a few weeks after normal hormone levels are achieved for patients. Sometimes it may take several months for the patient to achieve normal hormone levels. Such patients should continue their medications until the day of surgery and should definitely take their medications with a sip of water, even though they are hungry on the morning of surgery. If the patient is constantly taking aspirin, coraspin, kumadin, etc. if he is using blood-thinning medications, surgery should be performed first after stopping such medications and waiting at least 56 days.
If the decision to operate has been made to the patient, it should be examined by an anesthesiologist. After that, the patient should stay hungry after 24 o’clock the night before the operation, so that he does not eat or drink anything by mouth, including water, to give an example, he should enter the operation as if he were fasting. Patients with diseases such as sugar, high blood pressure and asthma should be exchanged ideas by the relevant branches, risks should be determined and recommendations should be taken. Patients who are going to have surgery should take their medications with a sip of water, even though they are hungry on the morning of surgery, if they are taking medications related to these diseases.
A written surgical permission must be obtained from the patients who will undergo surgery. For this purpose, the open forms specific to the surgery that are used and specially planned should be read and signed. It should be strictly documented that the patients allow the surgery by learning all the risks of the operation.
How reliable is a needle biopsy in a nodulated goiter?
During the examination, during the manual examination of the thyroid gland or ultrasound examination, bumps called ‘nodules’ with diameters ranging from a few Decil meters to a few cm can be detected. It is necessary to control and monitor how these cysts change over time. The reason is that these cysts are likely to turn into cancer in the long term, even if there is a low probability.
This probability is higher if the cyst has solid content, not liquid, and if hormone production is low (cold solid(water-filled) cyst on scintigraphy).
In such cases, it is not necessary to perform a needle biopsy on every patient. Especially in cysts that need to be needle biopsied; these are patients whose diameter is larger than 2 cm and patients who have calcification detected, even if the cyst diameter is smaller.
A thyroid biopsy is the removal of parts of the thyroid tissue with the help of a needle accompanied by ultrasound. The follow-up with this biopsy is very useful in terms of preventing unnecessary surgeries. But this method used is a method that also has limitations in terms of reliability.
In fact, in order for the biopsy to fully reflect the current condition, it is usually necessary to insert a needle in many places, many times. But the tissue sample taken in approximately one out of every four biopsies performed is not enough to give complete results.
If the result of the biopsy turned out to be cancer, this is almost always true, but when it says no, it’s a little more complicated. The reason is that it is technically impossible to catch all cancer cases with a biopsy. The reason for the main misconception in this case is that the biggest obstacle is the possibility that a small cancer islet may have jumped right around it while the needle is sinking into a point.
In the future follow-up of patients who have been given a clean (good result) needle biopsy report, it is later understood that one out of every 56 cases is actually cancer Jul. Although in a retrospective examination of patients who have undergone surgery and whose exact pathology has been found to have cancer, approximately one in every four patients has a needle biopsy report in their file that previously came out clean. Jul.