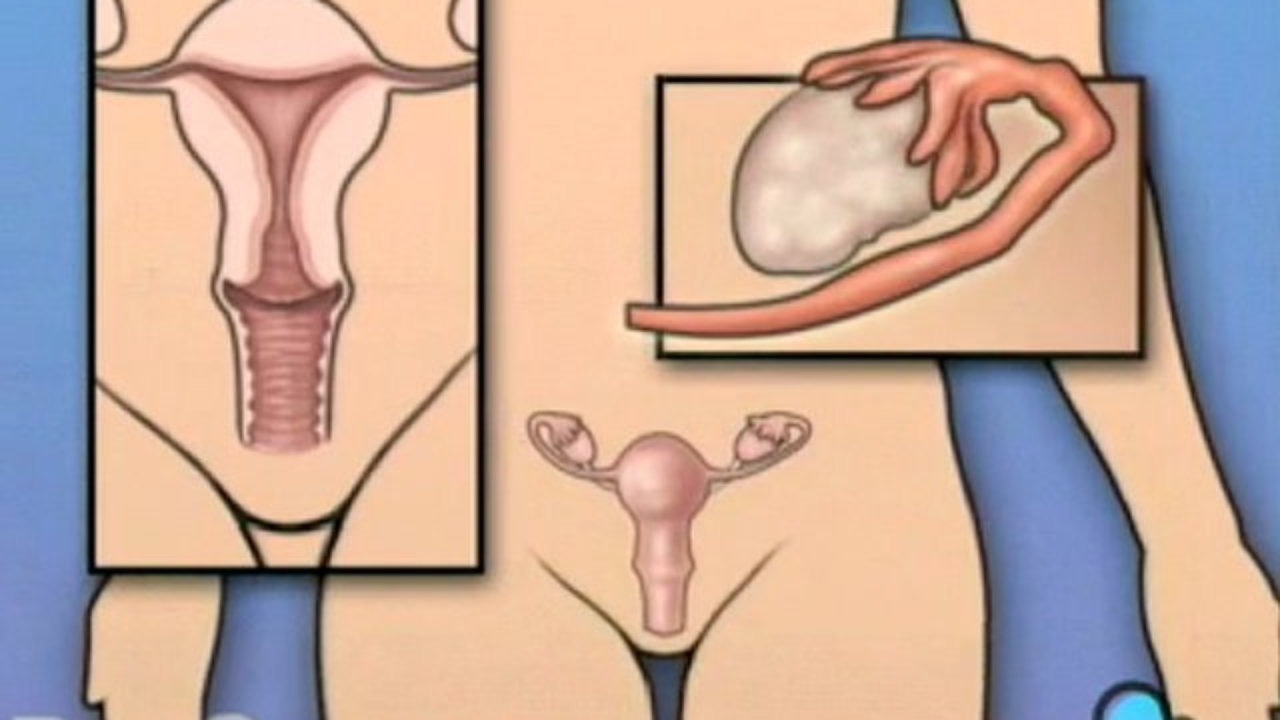
It is an operation to remove the uterus (uterus). Many gynecological problems can be solved with hysterectomy. But since it is a major surgical procedure, your doctor may recommend other forms of treatment first. Uterus: It is an organ formed of smooth muscle in the area surrounded by the pelvis (pel Novis), in which the baby develops during pregnancy. It provides the birth of the baby by contracting during the labor action. If there is no pregnancy, the layer that covers the inside of the uterus (endometrium) is excreted every month in the form of menstrual bleeding.What is a Hysterectomy?It is the removal of the uterus by surgery. It is one of the most frequent surgeries of the obstetrics and gynecology group. Some of the reasons for hysterectomy are:
Fibroids(benign Novae that develop from the smooth muscle of the uterus)
Endometriosis
Abnormal bleeding
Long-lasting pain caused by the uterus that cannot be responded to the applied treatments
Uterine prolapse
Cancer
Uterus removal surgeries do not include removal of ovaries and tubes. These organs can also be removed if there is a disease that requires them to be removed (salpingo-oophorectomy).
Types of Hysterectomy
The type of surgery varies depending on the examination findings, the disease that caused the operation, and the doctor’s choice.Abdominal Hysterectomy (Removal of the uterus from the abdomen): An incision is made in the lower abdomen starting from the skin to reach the uterus. Depending on the size of the uterus and the reason for the operation, the incision can be horizontal or vertical. The abdominal approach requires a longer recovery time than other types of hysterectomy. However, there are also some advantages. In this type of hysterectomy, the doctor can better see and evaluate the uterus and some other intra-abdominal organs. Especially in large urns, it is a good way to suspect cancer.Vaginal Hysterectomy (Removal of the uterus via the vagina): There is no incision in your abdomen in this method. Since the incision is located in the vagina, the recovery time is shorter than an abdominal hysterectomy.
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: The operation is performed partially or completely through a device called a laparoscope. A laparoscope is a thin instrument consisting of a light-filled lens system. It is inserted into the abdomen with a small incision (usually around the belly button). The doctor sees the patient’s intra-abdominal organs enlarged on the screen with the help of a laparoscope. Several more small incisions are made to insert auxiliary instruments into the operation. The duration of the operation is longer than abdominal and vaginal hysterectomies, and the patient’s recovery period is shorter.
What Needs to Be Done Before the Uterus Removal Surgery
In order to prepare for the surgery, you will be asked for a number of tests (blood, urine, lung film, heart graph “ECG”, etc.).
Again, a piece can be taken from the uterus during the preparation stage.
An enema can be performed the night before surgery and/or on the morning of surgery.
Antibiotics are made to prevent infection.
A plastic needle is inserted into your vein through the hand or arm so that the necessary fluids can be given during and after surgery.
In order for you to be comfortable during the operation, general (sleeping) or regional (lumbar) anesthesia is applied according to your condition.
A thin tube (urine probe) is inserted into your bladder to monitor your condition and adjust the amount of fluid.
Patients with hysterectomy stay in the hospital for several days. The duration of hospital stay depends on the type of surgery, whether a problem develops during or after surgery.
You should walk as early as possible after the operation. Just as walking will ensure the regulation of your blood circulation, balls will also help prevent the development of clots in your veins. If you are in the risk group, you will also be given medication to prevent the development of clots.
Know that you may have pain for a few days after the operation. Rest will speed up your recovery. If your doctor does not have additional recommendations, do not apply anything to the vagina for six weeks after surgery (such as showers, sexual intercourse, tampons), do not lift heavy weights, do not do heavy Oct. Even if you feel well before the end of the six weeks, do not engage in the opposite behavior without the control and recommendations of your doctor.As you recover, you can gradually increase your activities such as light physical activities, playing sports, driving.Having a hysterectomy does not mean that from a gynecological point of view, you will no longer have routine check-ups. If your cervix is stopping or you have had a hysterectomy due to cancer-a precursor cancer disease, Pap test screenings will continue.
Today, uterus removal surgery is one of the most common types of surgery. The operation of removing the uterus, which we call hysterectomy, is the process of removing the uterus. Fibroids, which we call tumor structures, are important factors in the removal of the uterus. Fibroids are the name given to benign tumors that develop in the smooth muscle tissue seen in the cervix. Nov. Fibroids are popularly known as ur. Dec. They are round, the size of a chickpea grain and pink in texture. Although it is seen in an average of 20% of women, it usually manifests itself between the ages of 25-35 Dec. With the appearance of fibroids, a number of events become self-evident. These occur in distressing situations such as groin pains, excessive bleeding, abundant and painful menstrual pains. Complaints that we call pressure also occur again through fibroids.
When is Surgery Necessary?Flesh particles found in the fetal bed, which we call polyps and which are located in the uterus, can cause conditions such as bleeding and menstrual irregularities. These polyps can be removed with vaginal surgical intervention. However, with an additional pathological condition in the patient, hysterectomy surgery may be required. Oct. Another condition, endometrial thickening, can cause cancer. This condition, which can usually be treated with hormonal medication methods, may require surgery if it does not show the necessary improvement. Excessive Bleeding Can Cause Anemia Excessive and irregular bleeding can cause anemia in the patient. Conditions such as fading of the person’s color, shortness of breath, palpitations may occur. A drug treatment is possible for these irregular bleeds. If this treatment method also does not respond, uterine removal surgery may be required.
Some conditions, such as menstrual pain being very severe and unbearable, difficult clotted periods, feeling extreme pain during intercourse, are indicative of a condition we call endometriosis. Endometriosis is a characteristic and pathological disorder. Medication treatments can help with recovery. But if the results cannot be obtained, Hysterectomy can be performed for patients who do not want children.
Especially manifested in difficult births, bladder, uterus and bowel sagging can be seen during menopause in cases such as increased abdominal internal pressure, genetic collagen tissue weakness. In cases of this type of external sagging, complaints such as urinary incontinence, uterine prolapse, fullness in the chamber are observed. In these types of cases, a procedure called vaginal hysterectomy, that is, the removal of the vagina with an incision made from the inside of the vagina, not from the outside, is performed. Hysterectomy may also be required in cases such as excessive blood loss after childbirth, uterine cancers.
The decision-making process for hysterectomy surgery is important. The doctor should clearly tell the patient about all possible consequences. If the patient is in the period of childbearing, the loss of childbearing status may cause psychological problems in the patient. In patients who want to give birth to children in the future, myomectomy surgery should be preferred first. This operation involves the removal of fibroids without removing the uterus.
Specialized doctors of the Gynecology and Obstetrics Department of Private Meltem Hospital successfully perform the uterus removal surgery and eliminate the disease.
One of the most common operations performed in gynecology is Hysterectomy, that is, uterine removal surgery, said Private Meltem Hospital Gynecology and Obstetrics Specialist Op. Dr. Bahar Aksünger states that 20% of women aged 25-35 have this tumor in the uterus, and its incidence increases with Decaying age. Dr. who gives information about tumors that require removal of the uterus. Aksunger continues his words as follows; ‘Fibroids, popularly known as ‘ur’, are round, chickpea grain size and pinkish color. Decapitated fibroids are the size of a chickpea. Fibroids, which manifest themselves with pain and bleeding in the uterus, should be treated urgently within the scope of symptoms.’ he says.
What are the Symptoms of a Tumor in the Uterus?
Fibroids, which are often seen in women, cause complaints such as irregular excessive bleeding, groin pains, anemia, abundant and painful menstrual periods with a progressive stage.’ he said Op. Dr. On the contrary; Fibroids, except anemia, cause ‘pressure’ complaints. When the pains we call ‘pressure’ are seen in the intestines, constipation, pressure in the urinary tract causes complaints in the urinary tract and kidneys.’ he says.
Op, which lists the reasons that require surgery. Dr. On the contrary; ‘Meat particles that we call polyps in the fetal bed located in the uterus can cause menstrual irregularities and bleeding. Normally, these polyps can be removed by a vaginal operation. However, if the patient has an additional pathological condition, hysterectomy surgery may be required. Oct. Again, the condition of thickening of the membrane, which we call endometrial, may also require surgery. In general, this condition can be controlled with hormonal drug therapy. But if this treatment does not show an effect, uterine removal surgery may be considered again. Conditions such as menstrual pain being too severe to bear, clotted and difficult menstruation, excessive pain during intercourse indicate the condition we call ‘Endometriosis’. Endometriosis, which is a pathological condition, is again being tried to be eliminated with drug treatments, and if the result cannot be obtained, hysterectomy is resorted to.’ he says.