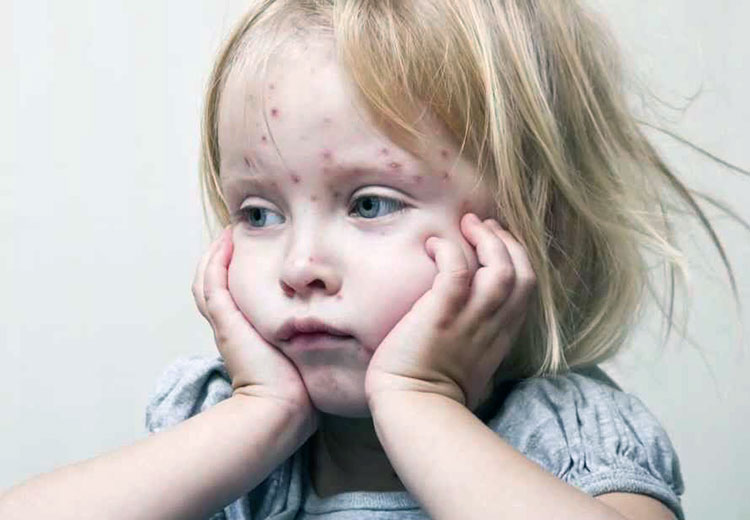
Measles is an infectious disease seen in children caused by a special virus called Morbilli. Measles, which is transmitted through the respiratory tract and direct contact with the patient, is a disease that requires attention due to its contagious nature. Measles, which is mostly seen in winter months, is seen in children between the ages of 3-10 on average. Measles, which is also seen in adults, is more common in children. Measles is a contagious disease that can cause serious problems in the school life of children or in the work life of adults.
Measles also has the ability to trigger some side diseases. It may cause diarrhea, middle ear infection, and inflammation of the lungs and larynx. It poses a danger to babies and pregnant women with weak measles resistance. It can even cause death. Measles can spread as an epidemic if necessary vaccination precautions are not taken.
What are the reasons why measles occurs?
Although the measles virus is transmitted by contact, it manifests itself when the body’s immune system is weak. The microbe that settles in the mouth or nasal cavity begins to reproduce there and spread throughout the body. The microbe spreads after approximately 10 days, causing the disease to occur. 15-17. The disease manifests itself fully on the following day. The disease is highly contagious until its 15th day. After the 15th day, the disease loses its contagious nature. The virus found only in urine maintains its continuity during this period. Rashes begin at the same time that disease-specific microbes appear in the blood and the healing process begins. The rash flakes off and the contagious period ends.
Symptoms of Measles
Symptoms of measles begin with the incubation period. It reproduces without symptoms for an average of 12 days. Before the 10th day, the phase we call rash begins. As the fever increases, small white spots appear in the mouth and inside the cheeks. During this process, which lasts for 2-3 days, the child appears reluctant and tired. He has no appetite, there is coughing and coughing. Although dry cough and watery eyes are symptoms of measles, it is at its most contagious during this period.
When the fever temporarily decreases, the period we call rash begins. The rashes are first pink in color with clear borders, then they swell slightly, increase in number and turn red. With the appearance of the rash, the fever rises again and the general condition of the child worsens. He constantly wants to lie down, cough and watery eyes continue.
On average, 3-4 days after the rash appears, the fever drops quickly. Coldness and malaise disappear. After flaking, the skin, especially around the face and neck, flakes off and the child appears to be completely healed.
How is measles treated?
First of all, in order to prevent the spread of measles, the patient should not be sent to crowded environments such as schools or nurseries. Attention should be paid to the patient’s cleanliness and nutrition. The patient’s room should be exposed to sunlight and kept clean. If the hygienic environment is not taken care of, this disease can progress and cause dangerous diseases such as pneumonia.
Measles vaccination is of great importance to get rid of measles. This vaccine must be received by consulting a pediatrician. Nowadays, measles vaccine is administered in two or three doses. The first measles vaccine for babies is given at 12 months of age. The second dose is administered to children aged 5-6. In some cases, the third dose can be given at the age of 12. If symptoms of measles occur, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician immediately. Precautions to be taken against measles will prevent the disease from reaching serious levels.