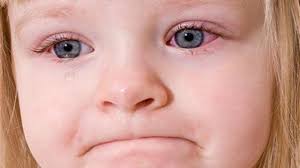
What Causes Watery Eyes in Children?
Watery eyes in children generally occur when a foreign object gets into the eye. Except that; Defects in the eyelids, eye pressure disease, eye scratching and tear duct obstruction are also manifested by symptoms of watering.
Defects in the eyelids may not only cause watering but also prevent vision. If conditions such as drooping eyelids, excessive skin folds, or narrow eyelid gaps make it difficult for the child to see, treatment should be applied without delay.
In addition, infections in the eyelids seen in babies and children also cause watering. Infections such as styes and similar swelling on the eyelid can cause pressure on the eyes. Pain caused by pressure, deformation in the tissues and amblyopia put a strain on the child. When these types of infectious diseases are noticed, they should be treated without delay.
Watery eyes in children may also occur as a result of allergic conditions. After the first 6 months, itching, redness, burning and watering in the eyes first brings to mind allergies. This condition, which usually affects both eyes, should be reported to a doctor and allergic factors should be avoided. Irritation to the eyes due to chemical effects may also cause watery eyes.
Other Causes of Watery Eyes
Congenital eye pressure also causes watering. Watery eyes are also an important symptom in children with scratched eyes. Since all these conditions require urgent treatment, family members should immediately consult a specialist when they notice this disorder in babies or children.
Tear duct obstruction is one of the most common eye diseases in infants and children. If persistent watering and burrs are observed in one or both eyes of the newborn baby, an ophthalmologist should be consulted, considering that the tear ducts may be congenitally blocked.
Tears are a secretion that keeps the eye constantly wet, cleans and protects it. It is secreted by the tear glands located on the outer part of the upper eyelid, just below the eyebrow. The excess part of the tears is transferred to the nasal cavity by the tear duct. The tear duct begins as two small holes in the inner corner of the lower and upper eyelids and extends downwards from there, opening into the nasal cavity. The reason why our nose runs when we cry is that large amounts of tears drain into the nose through this canal. Any blockage in these ejaculatory ducts is called ?tear duct blockage? It is defined as .
Tear Duct Blockage Treatment
Signs of clogging are; Unilateral or bilateral tearing in the eyes, swelling and redness in the sac between the eyes and nose, excessive discharge and pus formation in the morning, blurred vision due to continuous discharge, burning, stinging, itching and discomfort in the eyes.
Duct obstruction may be slightly more common in premature babies, boys and cesarean babies. While the baby is in the womb, the opening of the eye canals is covered with a membrane and usually opens during birth or a few days after birth. If not opened, these blockages may cause excessive watering and burrs in the eye. This situation is usually temporary. If watering and burring persist, it should be seen by a specialist doctor.
Treatment of blocked canal consists of several stages. First, massage is applied. The aim here is to open the blocked channel by increasing the hydrostatic pressure within the channel. In the meantime, necessary eye drops are also used. Massage and drop therapy are applied until the baby is 12 months old. During this time, it was observed that the canal was opened in 95% of the cases. However, if the canal obstruction does not improve by the age of 1 despite massage and drop treatment, an attempt is made to open the canal with a thin catheter under general anesthesia. This is a simple surgical procedure and can be performed when the baby is between 12-18 months. It is important not to delay treatment. Because this problem, which can be corrected with a simple intervention before the baby is 18 months old, requires surgery at older ages.